ChemistryWiki | RecentChanges | Preferences
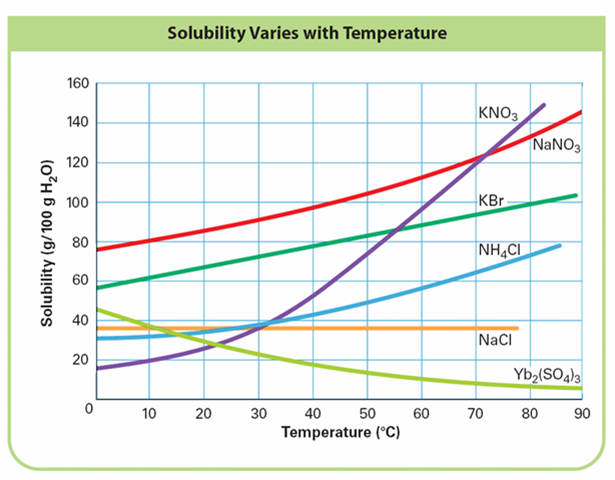
Unlike Molality and Molarity, solubility (S) only occurs at the saturation point. Therefore, the solution can only be a saturated solution (equilibrium exist between the solid and its hydrated ions) so solubility is a function of temperature. All solubility problem must specify the temperature of the solution to be investigated.
Solubility is usually expressed in units of g solute / g solvent where g solvent is usually "100.g H2O". Therefore, the equation for solubility is:
S = g solute / 100.g solvent , it should be written like:
So, Solubility problems are simply a set of ratios set equal to each other where one is the Solubility of the solution and the other is the gsolute over gsolvent:
S = gsolute / 100.g H2O = "X" gsolute / "Y" gH2O
The problem needs to provide 2 of the three piece of information in the equation and you solve for the third.