ChemistryWiki | RecentChanges | Preferences
Two Pillars of Chemical Reactions : Kinetic and Thermodynamics (Revised 2016)
In a chemical reaction, there are three questions that are commonly asked?
1. Does this chemical reaction occur?
2. How fast is the chemical reaction or how fast are the products formed (called rate of reaction)?
3. How do the reactants rearrange to make the product (called reaction mechanism)
Thermodynamics is the study of the movement (-dynamic) of heat/energy (thermo-) in chemical reaction. Almost all chemical reaction have either a total gain of heat/energy (or total loss of heat/energy) as the chemical reaction proceeds. This change in heat/energy determines if the chemical reaction occurs or not. Therefore, Thermodynamics answers Question #1 or does the chemical reaction occurs or not. It does not. however, explain how fast or the reaction mechanism of the chemical reaction.
How fast and what is the reaction mechanism for a chemical reaction is the domain of Kinetics. Therefore, Kinetics answers Question #2 & #3 and will be the topic we will deal with now.
Overview and Big Ideas of Kinetics
Kinetic data must be obtained experimentally
- Theory behind Kinetics is called Collision Theory (see notes below).
- Two reactant particles collide effectively (minimum energy and spatial orientation) to make products.
- If no Effective Collision (EC), no products formed, reactant stay as reactant
- Rate of reaction (answers Question 2 above). Two subsections :
- Rate Law (i.e., r = k [Reactant 1]x [Reactant 2]y)
- a mathematical approach to determining how "fast" you make product ([Reactant lost]/time, [Product gained]/time)
- Must be done by experiments
- Usually an AP concept
- Factors that change (usually increases) the rate of reaction
- Reaction Mechanism (answers Question 3).
- EC only can have only 2 particles collide, so most reactions are done in "sub-reactions" called Reaction step in specific sequence to get the overall chemical reaction to occur.
- Determining actual Reaction steps and their sequencing are beyond the scope of high school chemistry (1st year or AP) so these will be given.
- Kinetics Notes 3
Collision Theory
Rate of the chemical reaction:
Units of Rate:
Look at figure below
Activation Energy:
Activated Complex:
Do all collisions of reactants form products?
Effective Collisions
Two factors for an effective collision:
a.
b.
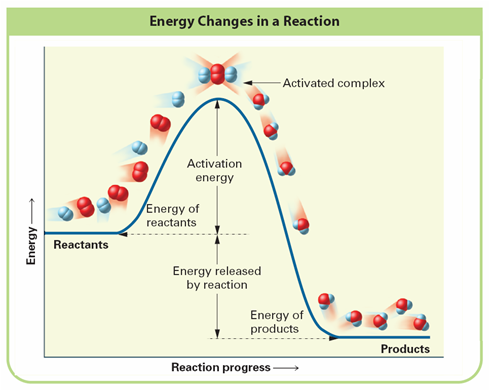
Look at figure, is the reaction exothermic or endothermic and why?
Kinetic Energy Diagrams
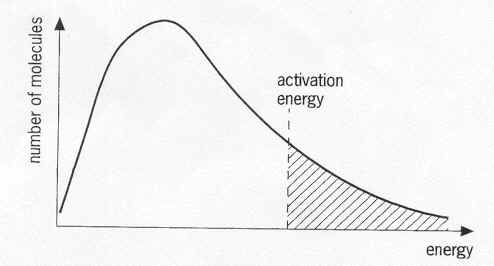
What is temperature?
Where are the particles that can have Effective Collisions (EC) on this diagram?

